What is the Enneagram?
The Enneagram is a holistic personality framework for understanding oneself and others. It is based on wisdom and experiential knowledge from many different psychological traditions and spiritual philosophies. Some theories and principles on which the Enneagram rests can be traced back to the ancient Greeks (Socrates and the Neoplatonists). Similar to the Enneagram, these traditions also “divided” people into nine main groups of certain personal characteristics and perspectives. From the mid-20th century, the Enneagram began to develop into the modern psychological model of today, based on the dedicated work of many individuals. The two persons who have been central for the development of today’s Enneagram framework are Oscar Ichazo and Claudio Naranjo, both originating from South America. Because the Enneagram has been developed through research, clinical work and studies of many different experts and centers, no person or organization can claim its ownership, nor is anyone its “founder”. For the same reason, the Enneagram also continues to develop, in terms of its depth, complexity, and understanding of the human. There are a few different narratives, but all are based on the same key elements and the overall structure, including the nine-headed symbol.
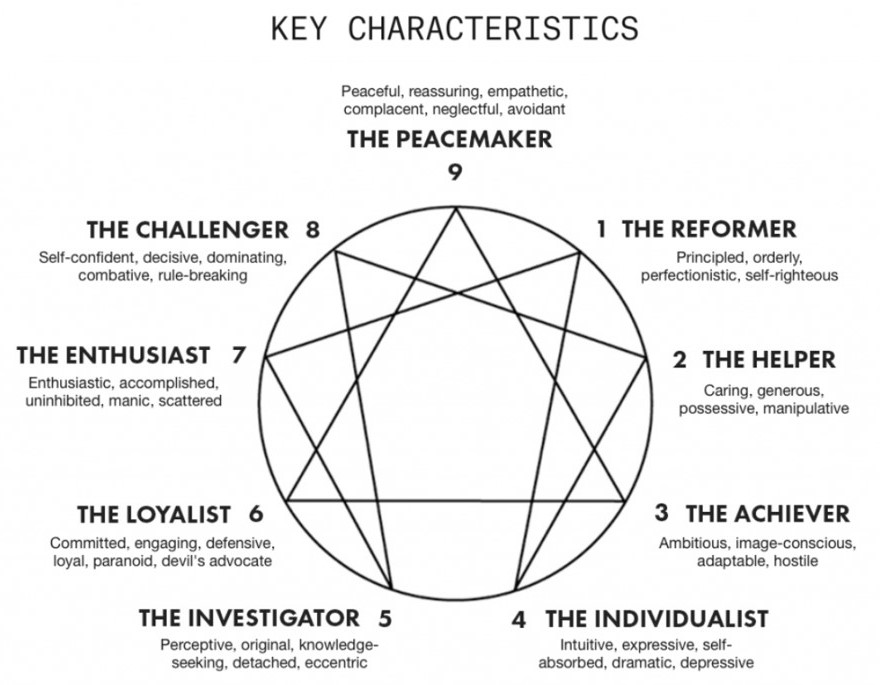
The nine personality types of the Enneagram
In essence, the Enneagram describes nine different personality types (sometimes also called strategies). Each personality type (or strategy) has its particular characteristics, in terms of general behaviors, desires, preferences, fears, and challenges. Thus, each personality type displays a certain habitual way of thinking, feeling and acting. Although each person will recognize him- or herself to some extent in ALL personality types, ONE personality type will feel most representative or well-reflective of one’s own unique personality. Thus, the Enneagram indicates how we tend to act out of pure habit, but also how we tend to act under stress, as well as how we may choose to act when we become more conscious of our tendencies.
Under stress, we are influenced by our “Stress-point”
Each person tends to adopt certain stress-induced behaviors, which are not typical for the type under “normal” conditions. Instead, these stress-induced behaviours are general features characteristic of another Type in the Enneagram. This other type is called our “Stress-point” or “Direction of disintegration”. For example, Type 7 tends to adopt certain stress-related behaviours that are generally associated with Type 1. Thus, Type 1 is the “stress-point” or “direction of disintegration” for Type 7. Thus, Type 7 may become irritable, self-critical and perfectionistic under stress; all of these charactersitics are general tendencies for a Type 1 personality.
When aware, we are influenced by our “Support-point”
Similarly, each person may adopt certain favorable or “supportive” behaviours that are more characteristic for another type. These supportive behaviours are thus not part of our habitual way of being or acting; yet, they can be fostered over time and become integrated within our personality as we grow in self-awareness and ability to be “present in the here and now”. The type, in which we find such favorable qualities for our own type, is called our “Support-point” or “Direction of integration”. For example, Type 7 can consciously choose to adopt favorable behaviours typical for Type 5, making Type 5 the “Support-point” (or “Direction of integration”) for Type 7. More specifically, Type 7 can choose to foster an ability to feel contentment with his/her understanding, as opposed to seeking to “fill one self up” with more ideas and knowledge.
Influenced by one of two “wings” (the types on each side)
Meanwhile, each personality type also has two so-called “wings”, which are the personality types on each side of one’s own type (on the Enneagram symbol). This means that your personality can be more or less influenced by the specific type on your left or right wing. For example, Type 7 may have a 6 wing or an 8 wing, which means that it shares certain qualities with either Type 6 or Type 8. Thus, depending on which is the most dominant wing for you, your personality will exhibit slightly different qualities. (The dominant wing can sometimes vary over your lifetime depending on your life circumstances.)
The three centers of intelligence – mental, emotional and physical
A fundamental part of the Enneagram is the division of human intelligences into three main centers, so-called intelligence centers. Of course, all people possess all three kinds of intelligences, but – based on our personality type – we tend to use and rely on one of these centers more than the others. In each intelligence center, three different personality types also dominate.
The mental intelligence and the Thinking Triad
- CENTER: The mental intelligence has its seat in the head and our thoughts.
- TYPES: The three personality types dominated by this intelligence are type 5, 6 and 7.
- BASIC DESIRES: Their main desires are: freedom and joy (type 7), security and support (type 6), and integrity and independence (type 5).
- CONCERNS: All these types are concerned with anxiety in different ways. Because they tend to experience lack of support and guidance in life, they tend to engage in behaviours that they believe will enhance their sense of safety and security.
- SEEKS: All of these types seek security in different ways. For example, Type 5 seeks knowledge and expertise; Type 6 tends to anticipate risks and avoid dangers; and Type 7 sees opportunities and plans for the future.
- TIME FOCUS: All of these three types are focused on the future (as opposed to the past or present).
- AVOIDANCE: The dominant emotion that these types try to deal with is Fear (generally fearing that their basic needs are threatened in some way).
The emotional intelligence and the Feeling Triad
- CENTER: The emotional intelligence has its seat in the heart and our emotions.
- TYPES: The three personality types dominated by this intelligence are Type 2, 3 and 4.
- BASIC DESIRES: Their main desires are: to be needed, appreciated and involved (Type 2); to be recognized, admired and successful (Type 3); and to be unique, deep and authentic (Type 4).
- CONCERNS: All of these types are concerned with their self-image, and may believe that the stories about themselves are their actual identity.
- SEEKS: All three types seeks attention, appreciation and/or recognition in different ways. For example, Type 2 focuses on meeting the needs of others; type 3 seeks to achieve high status and success for its own sake; and Type 4 seeks to be seen as original, deep and authentic by others.
- TIME FOCUS: All of these three types are focused on the past (as opposed to the present or future).
- AVOIDANCE: The dominant emotion that these types try to deal with is Shame (generally fearing that people will perceive them as “pretending to be some one other than they really are”).
The physical intelligence and the Instinctive Triad
- CENTER: The physical intelligence has its seat in the stomach and our physical needs and bodily instincts.
- TYPES: The three personality types dominated by this intelligence are type 8, 9 and 1.
- BASIC DESIRES: Their main desires are: independence, power and integrity (Type 8); inner peace, tranquility, and harmony (Type 9); and order, perfection, improvement and productivity (Type 1).
- CONCERNS: All three types are concerned with maintaining a resistance to reality, by creating boundaries for themselves, often in physical ways.
- SEEKS: All three types seeks autonomy in different ways. For example, Type 8 focuses on maintaining control or independence towards others; Type 9 seeks inner peace, fulfillment, and consensus (among others); and Type 1 seeks to achieve perfection, create order, and do “right”.
- TIME FOCUS: All of these three types are focused on the present (as opposed to the past or future).
- AVOIDANCE: The dominant emotion that these types try to deal with is Anger (or Rage), Agression and Repression (often being a frustration of not getting what he/she wants).
In summary, each personality type belongs to an intelligence center (mental, emotional or physical). Also, each type has a unique “stress-point” and “support-point”. Moreover, each personality type tends to have one wing that is more dominant than the other. (For example, a Type 7 personality may have a Type 6 wing or a Type 8 wing, which also influences his/her personality to some extent).
In the following sections, we will look at three types of social styles, as well as three types of coping or conflict management styles. Here, the nine personality types are divided into new triads!
Social behaviour and conflict management
The Enneagram also divides the nine personality types into two additional group categories, so-called triads, with three types in each group. These two triads are the Hornevian Groups and the Harmonic Groups.
- The Hornevian Groups – describe the social style of the nine personality types
- The confident (Type 7, 8 and 3): Want to act fast (can be a little impatient and eager); happy to act spontaneously with free rules; find it easy to talk to new people and often enjoy being in the center of social gatherings; gladly initiate projects and activities.
- The loyal (Type 1, 2 and 6): Want to help, take responsibility and meet the needs of others; seek cooperation and are happy to take on responsibilities and tasks; focus on how they can be helpful, fix and arrange things practically.
- The hesitating (Type 4, 5 and 9): Would like to have their own time and space; seek their own answers; focus on waiting, listening and observing in group situations; can refrain from social contexts, avoid being at the center and can be uncomfortable talking to new people.
- The Harmonic Groups – describe the coping style (or conflict management style) of the nine personality types
- The positive types (Type 7, 9 and 2): Have a positive attitude and like to see things from the bright side; rationalize around disappointments in a positive way; wants to make others feel good, as it will make them feel good too; do not want to feel negativity inside.
- The rational types (Type 1, 3 and 5): Are rational, logical, problem-solving, reason-based; try to be objective, fact-focused, consistent and effective; easily shuts off their emotions; focus on facts, goals, criteria, etc.
- The expressive types (Type 4, 6 and 8): React emotionally, often with strong reactions; want emotional reactions from others too; feel strongly both for what they like and dislike.
Health- or self-awareness levels
The Enneagram also uses a self-awareness scale that describes how well we function, depending on our level of self-awareness and inner harmony. Thus, when we are less self-aware and well-balanced (mentally and emotionally), we tend to act out our unfavorable tendencies more, for example acting out our fears, desires, and stress-related behaviours in more unhealthy ways.
Self-assessment test
If you wish to make an assessment of your own Enneagram personality type, there are several tests available on the internet. For an in-depth and comprehensive test, the full RHETI test is provided by the Enneagram Institue and can be purchased at an affordable price (12 USD) here. If you wish to take a shorter self-assessment, two well-made and useful tests are available for free, and can be accessed via the links below:
- The Riso-Hudson Enneagram Type Indicator (RHETI): The RHETI test is a short version of the complete original version of 144 questions. The RHETI test only covers 36-38 questions, but still provides a good assessment of the two or three most likely personality types for the test person. RHETI can be taken directly via this website: http://www.9types.com/rheti/index.php. Or it may be downloaded and printed as a pdf here: RHETI_SamplerHC. Note: The pdf also contains additional useful information for making the self-assessment.
- Quick Enneagram Sorting Test (QUEST): This test is also very useful for finding your personality type according to the Enneagram. The test can be opened and saved as a pdf via the following link: Quick Enneagram Sorting Test.
I (Anna) suggest that you do both self-assessment tests above (RHETI and QUEST) to get the most accurate results regarding your Enneagram personality type. I am also very happy to have a follow-up session with you to go through your test results, ask some in-depth questions for greater clarity and certainty, and for increasing your overall self-awareness.
Note: Remember, You are a UNIQUE person. The Enneagram is a tool and framework for supporting You in deepening your self-awareness, specifically by helping you to: (a) recognize “hidden aspects” (shadows) of your personality (such as subconscious beliefs, thought patterns, and disowned parts); (b) recognize and overcome fears, resistances, and unhealthy fixations or desires; and (c) understanding other people better and hereby support healthy and compassionate relationships with other people; and (d) to give guidance and direction for your unique personal growth and, if you wish, for your spiritual development.
Sources
- Riso, D R and R Hudson. 1999. The Wisdom of the Enneagram. The Complete Guide to Psychological and Spiritual Growth for the Nine Personality Types. Bantam Books. New Work. 389 pages.
- Timm, A and T Tornell. 2015. Self-insight. The key to developing yourself and others. Swedish title: Självinsikt. Nyckeln till att utveckla dig själv och andra. SYNK Publishing. Stockholm. 220 pages. (In Swedish)
- The Enneagram Institute. See under LEARN: https://www.enneagraminstitute.com/how-the-enneagram-system-works